학원/강의
*57일차 (함수)
pringspring
2022. 4. 18. 15:01
@function
*함수 선언/표현
*함수선언식 (Function Declaration)
- hoisting 처리됨
- 선언전에 호출 가능
- hoisting ? → 함수선언식 , var로 선언된 변수 등을 우선적으로 선언처리 하는 것
*함수표현식 (Function Expression)
- 변수에 함수를 대입
- 익명함수
- 끝에 세미콜론 작성하기
- hoisting 처리되지 않음.
- 선언전에 호출불가
*즉시실행함수 iife Immediately Invoked Fuction Expression
- 선언/호출 한번에 처리
<button onclick="test1();">함수선언식</button>
<button onclick="test2();">함수표현식</button>
<script>
(function(){
console.log("iife1 호출!");
})();
(function(){
console.log("iife2 호출!");
}());
(function(name){
console.log(`${name}님, 안녕하세요~`);
})('홍길동');
test1();
function test1(){
console.log("test1");
}
-----------------------------------------
const test2 = function foo(){
console.log("test2");
};
// foo();*매개인자 | 매개변수
*매개인자 (argument)
- 함수 호출부 값
*매개변수 (parameter)
- 함수 선언부 변수(공간)
**arguments 숨은 참조변수
- 호출부에서 전달한 매개인자를 가진 유사배열
- 화살표함수에서 이용불가
const test3 = function(){
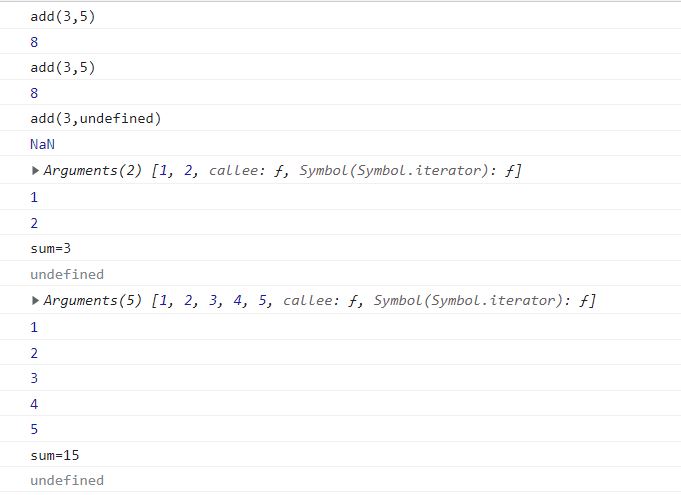
console.log(add(3, 5));
console.log(add(3, 5, 7)); // 매개변수가 없는 경우 무시
console.log(add(3)); // 매개인자가 없는 경우, 해당 매개변수는 undefined
console.log(add2(1, 2)); // 3
console.log(add2(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); // 15
};
const add2 = function(){
console.log(arguments);
let sum = 0;
for(let n of arguments){
console.log(n); // 요소
sum += n;
}
console.log(`sum = ${sum}`);
};
const add = function(a, b){
console.log(`add(${a}, ${b})`);
return a + b;
};
*리턴값
const test4=function(){
console.log(`리턴값 : ${foo()}`);
return 'fooooooooooooo';
};
const foo=function(){
console.log('foo');
};- 모든함수는 리턴값이 있다
- 명시적으로 선언하지 않았다면, undefined를 리턴함
→결과 :
foo
undefined
*나머지 파라미터
- 매개변수 선언부에서 사용
- 남은 매개인자를 모두 모아서 배열로 처리가능
- 선언되지 않은 변수
- 전개연산자와 모양은 같다
const test5=function(){
bar('홍길동', 33, '축구', '농구', '배구'); // ['축구', '농구', '배구']
bar('신사임당', 33, '클라이밍'); // ['클라이밍']
bar('윤봉길', 33); // []
};
const bar = function(name,age,...hobby){
console.log(`name=${name}`);
console.log(`age=${age}`);
console.log(`hobby=${hobby}`);
}
*@실습문제 : 계산기
* - calc('plus', 10, 20) 30 리턴
* - calc('minus', 100, 70) 30 리턴
* - calc('multiply', 5, 4, 3) 60 리턴
* - calc('divide', 100, 3) 33 리턴
const test6 = function (){
console.log(calc('plus', 10, 20));
console.log(calc('plus', 10, 20, 30));
console.log(calc('minus', 100, 70));
console.log(calc('multiply', 5, 4, 3));
console.log(calc('divide', 100, 3));
};
--------------------------------------------------------
const _calc = function(type, ...args){
let result;
switch (type) {
case "plus":
result = 0;
for(let n of args)
result += n;
return result;
case "minus":
result = args[0] - args[1];
return result;
case "multiply":
result = args.reduce(function(product, n, index){
// console.log(product, n, index);
return product * n;
});
return result;
case "divide":
return Math.floor(args[0] / args[1]);
default:
alert('지원하지 않는 연산 타입입니다.');
}
};
--------------------------------------------------------------
const calc = function(type, ...args){
const f = function(agg, n, index){
switch (type) {
case 'plus': return agg + n; // reduce 콜백함수의 리턴. 누적처리
case 'minus': return agg - n;
case 'multiply': return agg * n;
case 'divide': return Math.floor(agg / n);
}
};
const result = args.reduce(f);
return result; // calc리턴값
};
*화살표 함수 (arrow function)
- ES6 (ECMA2015)
- 익명함수를 function 키워드 없이 작성
- arguments 참조변수 사용불가
- 생성자 함수로 사용불가
- 함수자체의 this가 없고 부모 this를 가져와 사용한다
const test7 = () => {
console.log('test7');
console.log(koo(3, 7));
console.log(boo(5));
};
const koo = (a, b) => {
console.log(`koo(${a}, ${b})`);
return a + b;
};
const boo = a => a * 100;
const hoo = b => console.log(b);- 매개변수가 하나인 경우 , 매개변수부 괄호 생략가능
- 함수몸통부 코드가 리턴구문 한줄인 경우, {return ;} 생략가능
- 실행코드가 한줄인 경우도 {return ;}생략가능
→결과 :
test7
koo(3,7)
10
500
*중첩된 함수
- 함수 안에 선언할 수 있다
const test8 = (a) => {
const f = (n) => (n < 10 ? `0${n}` : n);
console.log(f(5));
console.log(f(10));
};→결과 :
05
10
*함수 고급 - 매개인자 처리
- 함수는 1급 객체
- 값으로써 처리가 가능
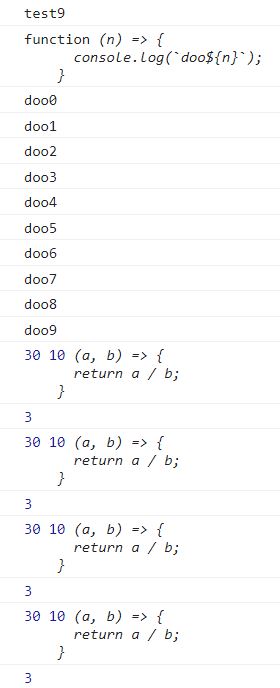
const test9 = () => {
console.log('test9');
const doo = (n) => {
console.log(`doo${n}`);
};
funcExecuter(doo);
};
+)실습문제 : calc
숫자 2개와 계산함수를 함께 전달해서 결과값을 출력
(호출코드 30,10)
const test9 = () => {
console.log('test9');
const doo = (n) => {
console.log(`doo${n}`);
};
funcExecuter(doo);
const add = (a, b) => a + b;
const subtract = (a, b) => a - b;
const multiply = (a, b) => a * b;
const divide = (a, b) => a / b;
console.log(calculator(30, 10, add));
console.log(calculator(30, 10, subtract));
console.log(calculator(30, 10, multiply));
console.log(calculator(30, 10, divide));
};
const calculator = (x, y, calc) => {
calc = (a, b) => {
return a / b;
};
console.log(x, y, calc);
return calc(x, y);
};
const funcExecuter = (func) => {
console.log(typeof func, func);
for(let i = 0; i < 10; i++){
func(i);
}
};
*함수고급 - 리턴값 처리
- 함수 호출 결과가 함수일 수 있다
const test10 = () => {
// const f = funcMaker();
// console.log(typeof f, f);
// for(let i = 0; i < 10; i++)
// f(i); // 매개인자 i
// 안녕, xx야~ 를 출력하는 sayHello
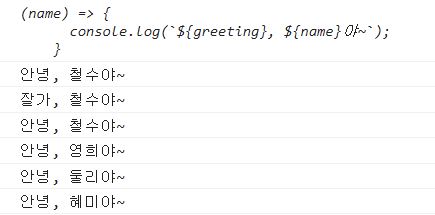
const sayHello = funcMaker2('안녕');
console.log(sayHello);
sayHello('철수'); // 매개인자 철수
// 잘가, xx야~ 를 출력하는 sayGoodbye
const sayGoodbye = funcMaker2('잘가');
sayGoodbye('철수');
const friends = ['철수', '영희', '둘리', '혜미'];
friends.forEach((name, index) => {
sayHello(name);
});
};
const funcMaker2 = (greeting) => {
return (name) => {
console.log(`${greeting}, ${name}야~`);
};
};
const funcMaker = () => {
return (i) => {
console.log(`qoo${i}`);
};
};
ex)실습문제 - tagMaker (test11)
- tagMaker 호출시 특정태그를 생성할 수 있는 함수리턴
- test11 함수 안에서 생성될 변수(함수)
- writeP
- writeSpan
- writeMark
- writeButton
→ 결과 :
(data) => {
return `<${tagName}>${data}</${tagName}>`;
}